 Mybatis基本流程及配置文件解析
Mybatis基本流程及配置文件解析
本文详细介绍了MyBatis的基本流程,包括配置文件加载、SqlSessionFactory工厂创建等,并解析了常用配置,如日志输出、数据源管理、类型别名等。此外,还讨论了动态SQL的实践,包括条件查询、SQL片段抽取等技巧。
# Mybatis 基本流程
1、利用 Resources 工具类加载配置文件,并转换成 输入输出流
2、利用解析的配置,创建 SqlSessionFactory 工厂
3、生产 SqlSession
4、SqlSession 调用方法
# Mybatis 配置文件分析
# sqlMapConfig.xml
# MyBatis 核心配置文件层级

# MyBatis 常用配置解析
输出日志,在 sqlMapConfig.xml 添加如下配置:
<settings>
<!-- 输出日志 -->
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING" />
</settings>
2
3
4
1)environments 标签
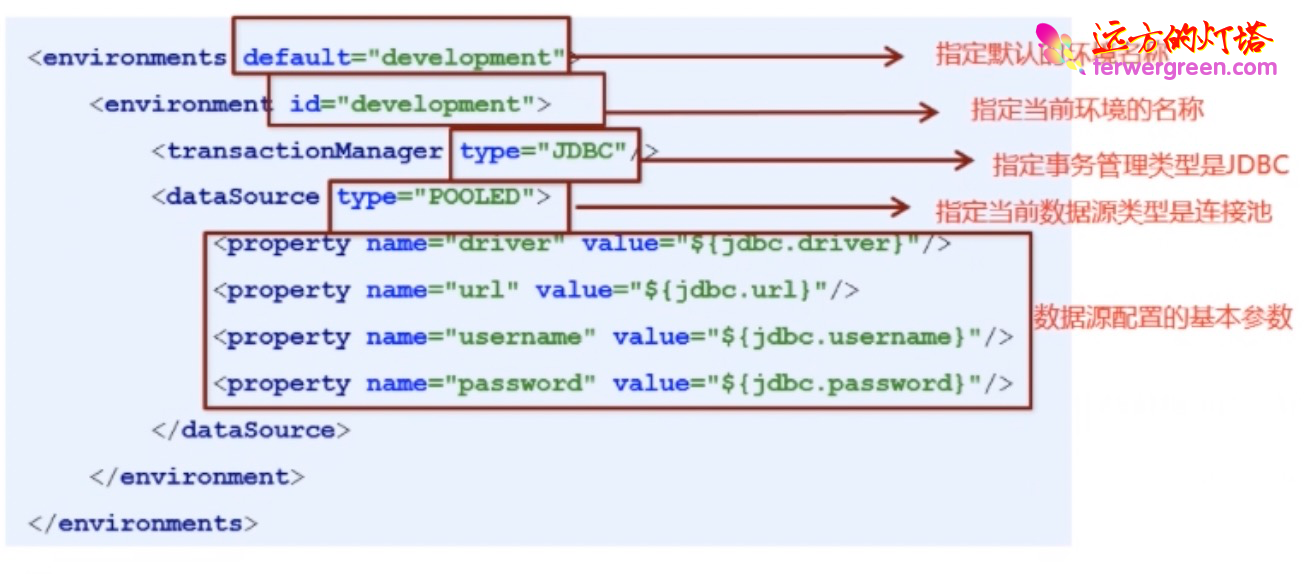
事务管理器( transactionManager )类型有两种:
JDBC:直接使用 JDBC 的提交和回滚设置,依赖于从数据源得到的链接来管理事务的作用域
MANAGED:几乎不做事。不提交事务也不会回滚。让容器(例如 JEE 的应用服务器的上下文)来管理事务的整个生命周期。
默认情况下会关闭链接,然而一些容器不希望这样,需要配置 closeConnection 的属性为 false 来阻止它的默认关闭行为。
数据源( DataSource )有三种:
- UNPOOLED:每次请求都打开和关闭链接
- POOLED:采用连接池管理 JDBC 链接
- JNDI:为了配合 EJB 容器使用,容器可以集中在外部配置数据源,然后放置一个 JNDI 的上下文引用
2)mapper 标签
作用是加载映射,加载方式有以下四种:
使用相对类路径的引用,例如:
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml" />1使用 URL,例如:
<Mappper url="file:///var/mapper/AuthorMapper.xml" />1使用接口实现类的全限定类名,例如:
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.AuthorMapper" />1使用包名称,例如:
<package name="org.mybatis.builder" />1
3)Properties
习惯性将数据量配置信息单独配置在 jdbc.properties 文件中
jdbc.dirver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/zdy_mybatis?characterEncoding=utf8
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123456
2
3
4
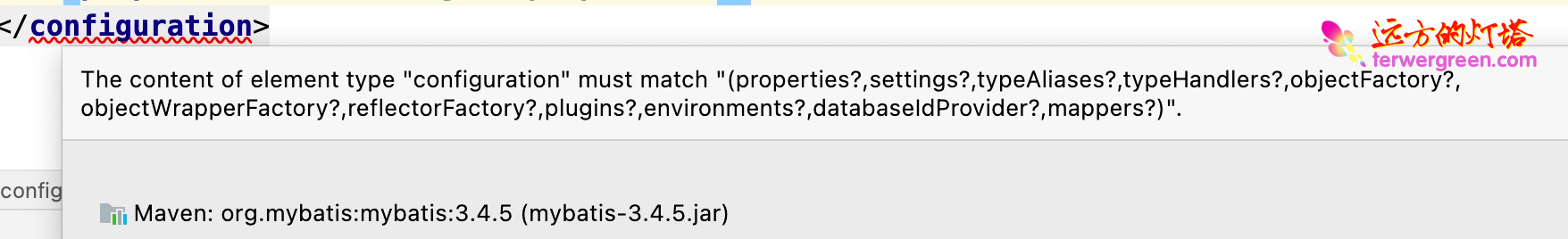
<properties resource="jdbc.properties"/>

注意顺序:properties 必须在最前面,否则会报如下错误
4)typeAliases 标签
类型别名是为 Java 类设置一个短的名字。原来的类型配置如下:
<select id="findAll" resultType="com.terwergreen.pojo.User">
select * from user
</select>
2
3

配置 typeAliases,为 com.terwergreen.pojo.User 指定别名 user
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.terwergreen.pojo.User" alias="user"/>
</typeAliases>
2
3
<select id="findAll" resultType="user">
select * from user
</select>
2
3

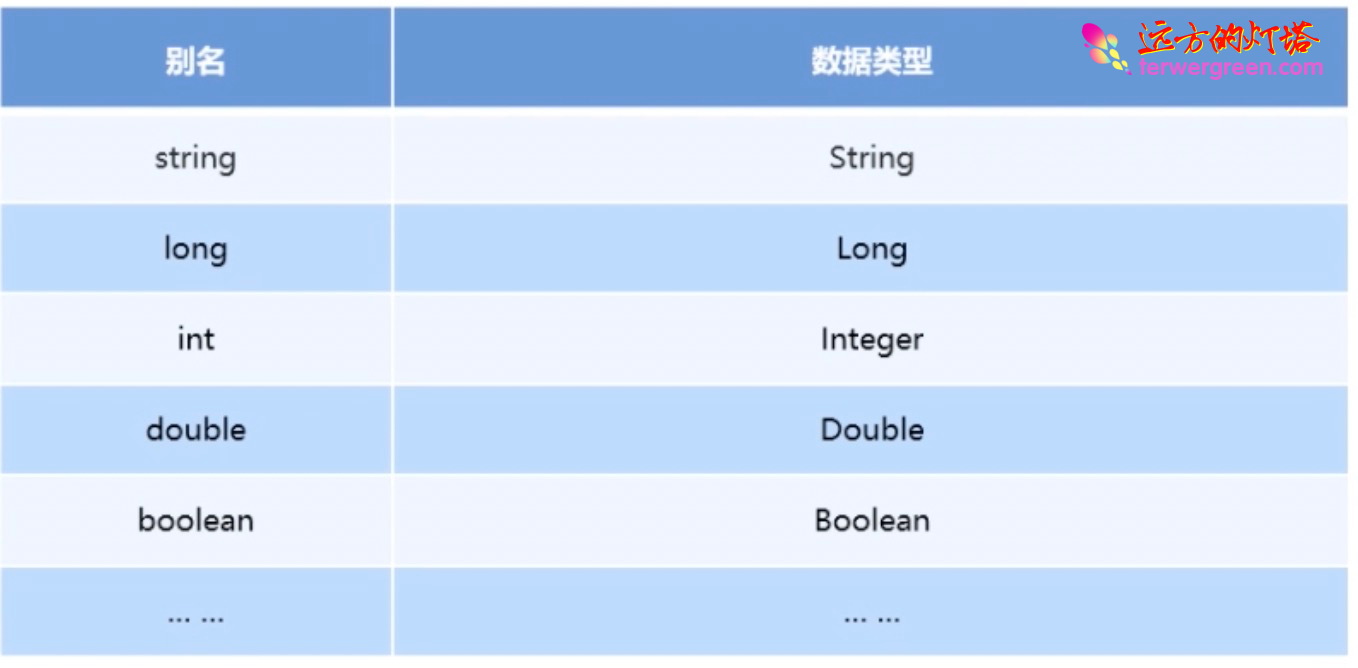
上面是我们自定义的别名,Mybatis 默认已经为我们设置好了一些别名:
如果实体类较多,上面方法不可取,可以使用指定包名的方式
<!-- 为实体的全限定类名取别名 -->
<typeAliases>
<!-- 给单独的实体起别名 -->
<!-- <typeAlias type="com.terwergreen.pojo.User" alias="user"/> -->
<package name="com.terwergreen.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
2
3
4
5
6
批量起别名:该包下所有类本身的类名,不区分大小写
# mapper.xml
1)动态 SQL
动态 SQL 语句概述
https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/dynamic-sql.html
# 动态 SQL 之 <if>
根据实体类的不用取值,使用不同的 SQL 进行查询
<!-- 多条件组合查询用户:if案例 -->
<select id="findByCondition" parameterType="user" resultType="user">
select * from user where 1=1
<if test="id!=null">
and id=#{id}
</if>
<if test="username!=null">
and username=#{username}
</if>
</select>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 动态 SQL 之 where
<!-- 多条件组合查询用户:where案例 -->
<select id="findByConditionWhere" parameterType="user" resultType="user">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="id!=null">
and id=#{id}
</if>
<if test="username!=null">
and username=#{username}
</if>
</where>
</select>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
同时设置 id 和 username 之后,日志如下:
public void test7() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
IUserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setUsername("tyw");
List<User> userList = userDao.findByConditionWhere(user);
for (User user2 : userList) {
System.out.println(user2);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
==> Preparing: select * from user WHERE id=? and username=?
==> Parameters: 1(Integer), tyw(String)
<== Columns: id, username
<== Row: 1, tyw
<== Total: 1
User{id=1, username='tyw'}
2
3
4
5
6
# 动态 SQL 之 foreach
循环执行 SQL 的拼接动作。例如:select * from user where id in(1,2,4)
测试代码
public void test8() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
IUserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
Integer[] ids = new Integer[]{1, 2, 4};
List<User> userList = userDao.findByIds(ids);
for (User user2 : userList) {
System.out.println(user2);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
配置如下
<!-- 多值查询:foerach案例 -->
<select id="findByIds" parameterType="list" resultType="user">
select * from user
<where>
<foreach collection="array" open="id in (" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
日志如下:
==> Preparing: select * from user WHERE id in ( ? , ? , ? )
==> Parameters: 1(Integer), 2(Integer), 4(Integer)
<== Columns: id, username
<== Row: 1, tyw
<== Row: 2, 张月
<== Row: 4, haha
<== Total: 3
User{id=1, username='tyw'}
User{id=2, username='张月'}
User{id=4, username='haha'}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
foreach 各项的含义如下:
<foreach> 用于遍历几乎
- collection:要遍历的集合元素,不能带有#{}
- open:语句开始部分
- close:结束部分
- item:遍历的元素生成的变量名
- sperator:分隔符
# SQL 片段抽取
可以将重复 sql 抽取出来放在 sql 标签中,使用时候用 include
<!-- 抽取sql片段简化编写 -->
<sql id="selectUser">select * from user</sql>
2
使用
<!-- 根据ID查询用户 -->
<select id="findById" parameterType="int" resultType="user">
<include refid="selectUser"></include> where id=#{id}
</select>
2
3
4
测试:
/**
* sql抽取测试
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void test9() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
IUserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
User user2 = userDao.findById(1);
System.out.println(user2);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
日志如下:
==> Preparing: select * from user where id=?
==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
<== Columns: id, username
<== Row: 1, tyw
<== Total: 1
User{id=1, username='tyw'}
2
3
4
5
6
文章更新历史
2024/04/24 同步文章到其他平台
2022-08-30 feat:初稿
